
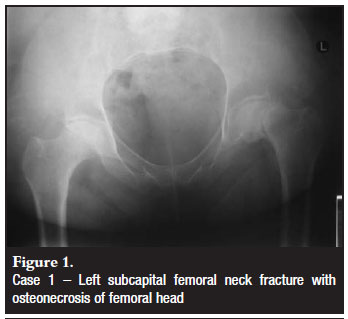
High morbidity and mortality associated with hip and pelvic fractures after trauma has been well documented. Prognosis is varied, but is complicated by advanced age, as hip fractures increase the risk of death and major morbidity in the elderly. Replacing the femoral head is achieved with either hemiarthroplasty or total hip arthroplasty. Internal fixation can be performed with multiple pins, intramedullary hip screw (IMHS), crossed screw-nails or compression with a dynamic screw and plate. The treatment options include non-operative management, internal fixation or prosthetic replacement. Significant complications such as avascular necrosis (AVN) and non-union are very common without surgical intervention.
Avascularity of the femoral head is more common with fractures that are cranially situated in the femoral neck.

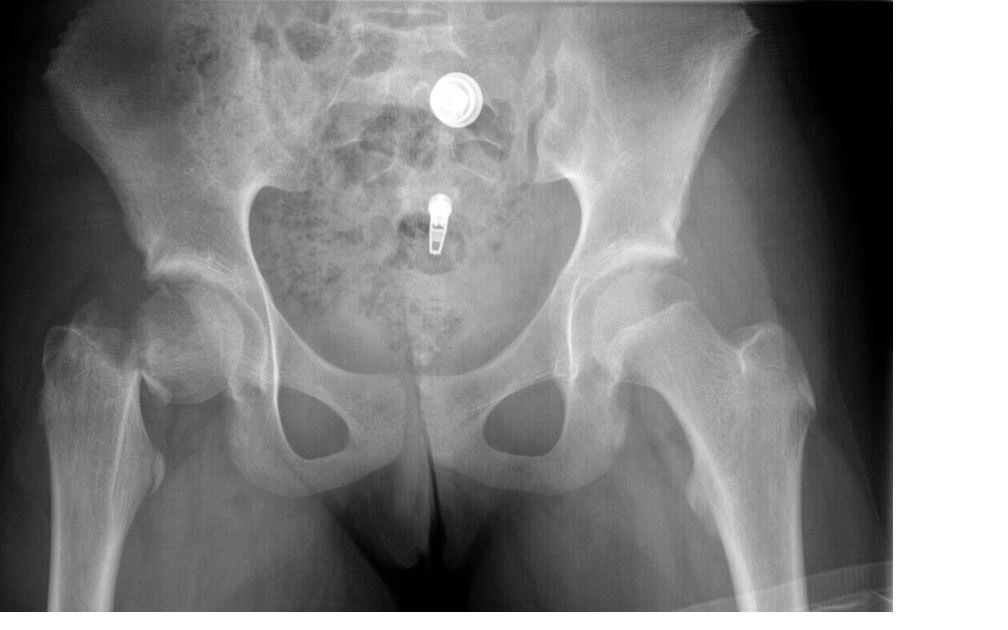
Since disruption of blood supply to the femoral head causes significant morbidity, diagnosis and classification of these fractures is important. Subsequent images revealed that the patient had surgical management of this fracture resulting in the placement of an Austin-Moore prosthesis.įemoral neck fractures are a subset of proximal femoral fractures. The femoral neck is the weakest part of the femur. The distal femur was displaced cranially and laterally. There was a fracture of the high femoral neck on the right. ODIN Link for Femoral Fracture images (Pre and Post-Op), Figure 14.12A and B: Figure 14.12A X-ray of the femur, pre-operative femoral neck fractureįigure 14.12B X-ray of the femur, post-operative arthroplasty Imaging Assessment


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
